2021
Stream processing technologies such as Kafka, Spark, Flink
Distributed caching technologies (Hazelcast, Gemfire,
- public and private cloud development using platforms such as Kubernetes, Cloud Foundry and AWS
- Spring Boot 1.x and 2.x
- Scripting languages such as Groovy, Python, etc.
- Metrics / Logging Tools (Grafana, Splunk, Prometheus, Cortex, Micromete
- Modern development practices such as Agile / Scrum, Git, CI / CD
- JS unit testing tools & frameworks (Jest, Mocha, etc.)
- RESTful API consumption
- Build and packaging tools (npm script, Webpack, Babel)
SAGA | Microservices Architecture Patterns
The Saga Pattern is as microservices architectural pattern to implement a transaction that spans multiple services.
A saga is a sequence of local transactions. Each service in a saga performs its own transaction and publishes an event. The other services listen to that event and perform the next local transaction. If one transaction fails for some reason, the saga also executes compensating transactions to undo the impact of the preceding transactions.
Types of Sagas
There are two types of Sagas:
Orchestration-Based Saga
In this approach, there is a Saga orchestrator that manages all the transactions and directs the participant services to execute local transactions based on events. This orchestrator can also be though of as a Saga Manager.
Choreography-Based Saga
In this approach, there is no central orchestrator. Each service participating in the Saga performs their transaction and publish events. The other services act upon those events and perform their transactions. Also, they may or not publish other events based on the situation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Saga Pattern
The main benefit of the Saga Pattern is that it helps maintain data consistency across multiple services without tight coupling. This is an extremely important aspect for a microservices architecture.
However, the main disadvantage of the Saga Pattern is the apparent complexity from a programming point of view. Also, developers are not as well accustomed to writing Sagas as traditional transactions. The other challenge is that compensating transactions also have to be designed to make Sagas work.
In my opinion, Sagas can help solve certain challenges and scenarios. They should be adopted or explored if the need arises. However, I would love to hear if others have also used Saga Pattern and how was the experience? What frameworks (if any) did you use?
Introduction
In this article, we are going to discuss the Microservices Architecture pattern - SAGA pattern. This article can be used by beginners, Intermediate and Professional.
We are going to cover,
- What is SAGA Pattern?
- Real World use Case
- Types of SAGA pattern
- Choreography – Basic
- Orchestration - Basic
What Is SAGA Pattern?
Microservices are very popular and vastly used in today's technology world. Implementing microservices is easy but complications start when the distributed transaction comes into the picture.
SAGA patterns introduce to solve this problem.
Consistency plays a very important role in any transaction. I mean transactions should execute all or nothing.
Now think about multiple microservices with their database. We need to roll back all completed transactions in case of any microservice failed in between to maintain data consistency to make our business reliable, sustainable, and reach to desire outcome.
USE CASE
Let us assume that we have an online restaurant ordering system.
For Online Restaurant system might have below microservices,
- Order Services – Place order service
- Payment Service – Payment service for payment
- Restaurant Service – Select restaurants and select dishes.
- Delivery Service – Deliver order.
How will they interact?
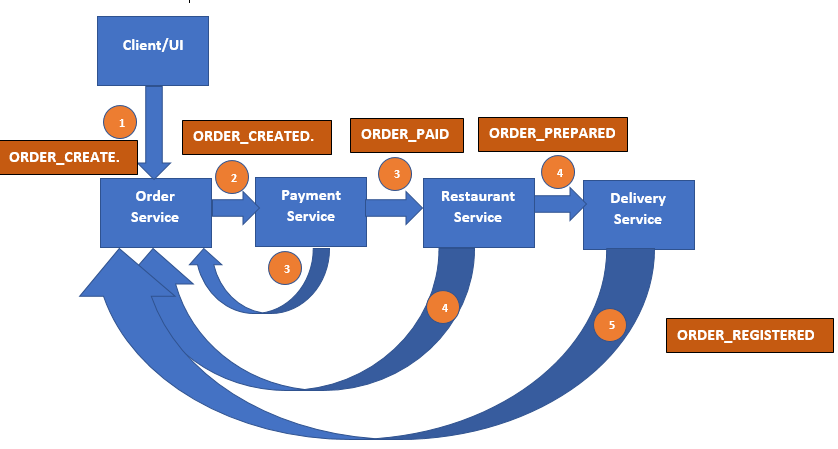
The below image will explain the process,
- Client/ UI placed Order using Order service.
- Payment service confirmed about payment received and notify to order service and Restaurant service.
- Restaurant service checks the availability of items and notifies to Order Service and next service Delivery service.
- Once delivery is done, the Delivery service notifies to Order Service.
In case of any microservices failed, the SAGA pattern will roll back transaction from all other microservice to make sure consistency.
Types of SAGA
SAGA pattern can be implemented using the below 2 ways,
- Choreography – Event-based
- Orchestration – Command-based.
Choreography – Event-based
In choreography, each microservices interact with each other through the event. In this case, we do not have any centralized service or coordinator.
For the event, we can use event sync like RabbitMQ or MSMQ, etc.
Let's try to discuss the same use case for Choreography.
As we know its event-based and all microservice interact using common queue like RabbitMQ, MSMQ, etc
As you can see in about images, Each stage has an event and this event registers in a common queue. The next subsequence service will be executed based on the event completed and register in the queue.
Eg.
- ORDER_CEATE Event register when order placed. Once Order Created ORDER_CREATED event fire.
- The payment service will see this event and start verifying payment status. If it's paid ORDER_PAID event trigger and notify to Order service and Restaurant service.
- Restaurant service checks the availability of items and registers vent ORDER_PREPARED.
- Once Order delivers ORDER_REGISTERED event fire and notifies to order service.
Choreography - Proc/Cons
- It is very simple to start as it doesn’t have any coordinator.
- No single point of failure.
- Complex in the large number of microservice and huge documents required to understand interaction flow of microservices.
- Integrate testing is difficult.
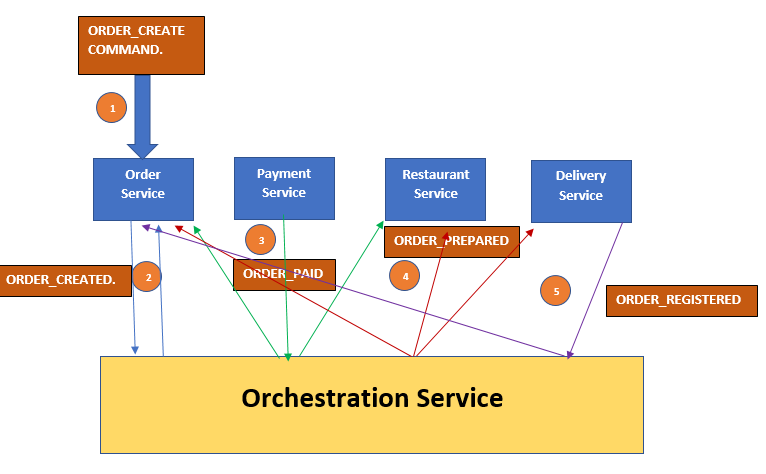
Orchestration – Command-based.
It is a centralized service to manage transactions of all services and flow.
The orchestration tells each microservices which operations to perform and in case of failure, it also sends messages to different microservices for the rollback of the transaction.
It also manages the state of each task through the state machine.
Let’s discuss the same Restaurant service example here.
It is the command-based approach. All command is handled by centralized Service called “Orchestration Service” This service maintain the state of each microservices and give command accordingly.
Orchestration - Proc/Cons
- Easily to add new microservices hence highly scalable.
- No possibility of cyclic dependency between microservices
- Single point of failure.
- Complex due to manage state tasks.
In the next article, I will try to explain the same concept through .net core code. I hope you enjoyed this article and find it useful.
Microservices are often integrated using a simple protocol like REST over HTTP. Other communication protocols can also be used for integration like AMQP, JMS, Kafka, etc.
The communication protocol can be broadly divided into two categories- synchronous communication and asynchronous communication.
- Synchronous Communication
RestTemplate, WebClient, FeignClient can be used for synchronous communication between two microservices. Ideally, we should minimize the number of synchronous calls between microservices because networks are brittle and they introduce latency. Ribbon - a client-side load balancer can be used for better utilization of resource on the top of RestTemplate. Hystrix circuit breaker can be used to handle partial failures gracefully without a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem. Distributed commits should be avoided at any cost, instead, we shall opt for eventual consistency using asynchronous communication.
- Asynchronous Communication
In this type of communication, the client does not wait for a response, instead, it just sends the message to the message broker. AMQP (like RabbitMQ) or Kafka can be used for asynchronous communication across microservices to achieve eventual consistency.
In Orchestration, we rely on a central system to control and call other Microservices in a certain fashion to complete a given task. The central system maintains the state of each step and sequence of the overall workflow. In Choreography, each Microservice works like a State Machine and reacts based on the input from other parts. Each service knows how to react to different events from other systems. There is no central command in this case.
Orchestration is a tightly coupled approach and is an anti-pattern in a microservices architecture. Whereas, Choreography’s loose coupling approach should be adopted where-ever possible.

Comments
Post a Comment